Course Introduction
Professional certification
Google Professional Cloud DevOps Engineer
Implement CI/CD, apply SRE discipline, and keep services reliable on Google Cloud. This guide mirrors the official exam objectives with practical delivery, observability, and optimization workflows.
Want to pass faster?
Get practice tests + the latest deals/discount codes
Get the latest from Cloud-Edify
Get two free courses coupons. Curated learning content, tools, and deal alerts—straight to your inbox.
CI/CD architecture
Design pipelines with Cloud Build, Deploy, and Artifact Registry across hybrid targets.
Secure delivery
SLSA, Binary Authorization, and secrets management embedded into pipelines.
SRE practices
SLIs/SLOs, error budgets, and reliability targets that guide release velocity.
Observability & FinOps
Telemetry, incident response, and cost optimization across services.
Exam Guide + SRE Playbook
Focus on secure CI/CD delivery, measurable reliability, and observability practices that keep production stable while shipping fast.
Exam Overview
Length: 2 hours
Format: 50-60 multiple choice and multiple select questions
Prerequisites: scripting, IaC with Terraform, and container orchestration on GKE
Focus: SRE principles plus practical CI/CD, monitoring, and reliability automation
Exam Domains (5 Sections)
Open each section for key objectives.
1) Bootstrapping and maintaining the organization
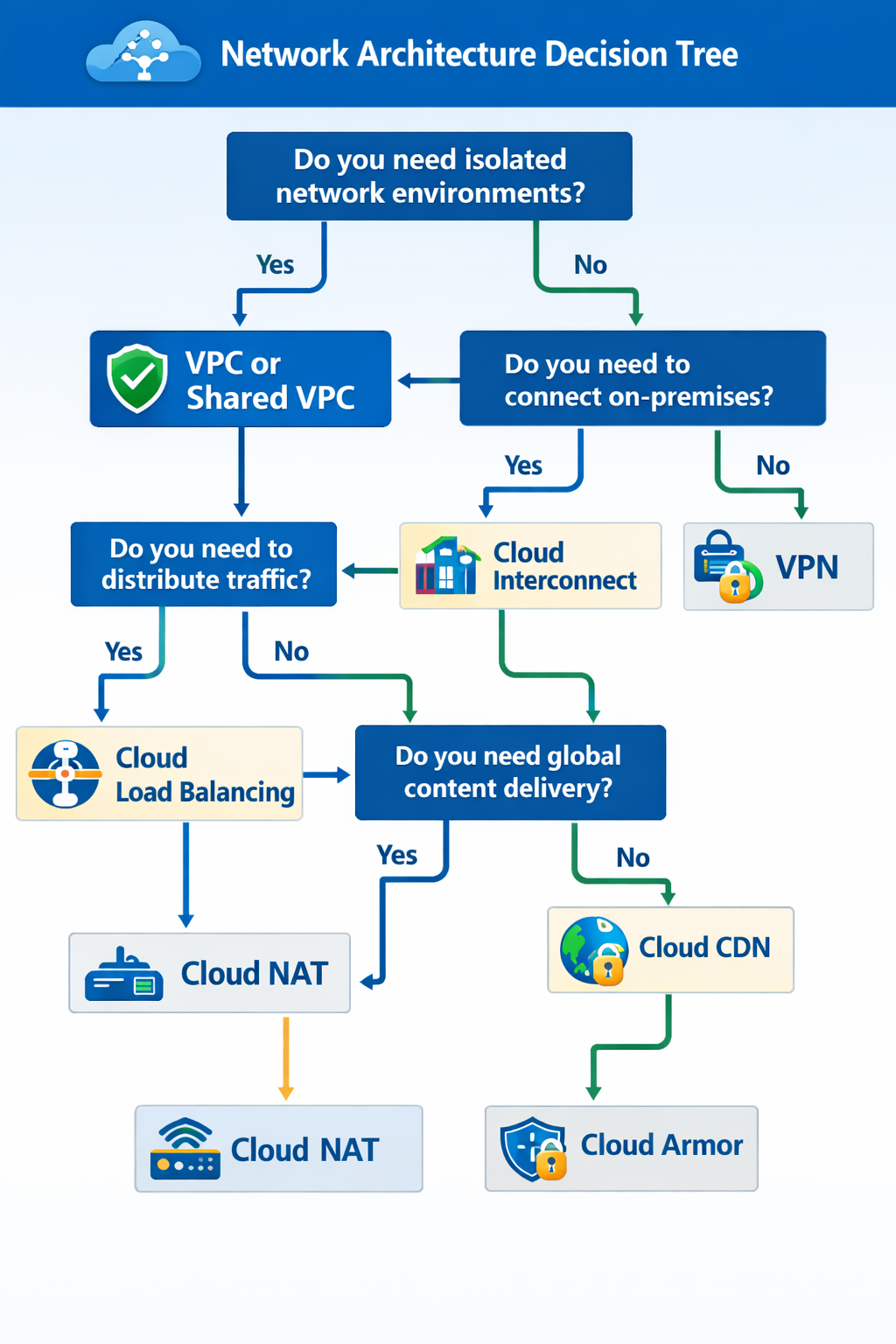
Resource hierarchy and IAM: folders, projects, Shared VPC, and least privilege policies.
Workload identity: standard for GKE service access without long-lived keys.
IaC foundations: Terraform, Config Connector, and GitOps workflows for consistent environments.
Secure dev environments: Cloud Workstations, Cloud Shell, Gemini Code Assist.
2) Building and implementing CI/CD pipelines
CI: Cloud Build triggers, cloudbuild.yaml, Artifact Registry, vulnerability scanning.
CD: Cloud Deploy, Skaffold, and Kustomize for repeatable releases.
Strategies: blue/green, canary, rolling updates, and traffic splitting.
Supply chain security: Binary Authorization and SLSA provenance.
3) Applying SRE practices
SLI/SLO/SLA: define targets and measure reliability with error budgets.
Incident response: blameless postmortems, fast rollback, and toil reduction.
4) Observability and troubleshooting
Logging: structured logs, log sinks to BigQuery, Pub/Sub, or Cloud Storage.
Monitoring: golden signals, alerting policies, uptime checks, Managed Prometheus.
Tracing: Cloud Trace for microservice latency analysis.
5) Optimizing performance and cost
Cost levers: committed use discounts, Spot VMs, and GKE Autopilot right-sizing.
Performance: Active Assist recommendations and Cloud Profiler for CPU and memory insights.
Exam Focus
- Measure reliability with SLIs, SLOs, and error budgets.
- Build secure, automated CI/CD pipelines with policy controls.
- Instrument services with logs, metrics, and traces.
- Balance reliability, release velocity, and cost efficiency.
Cheatsheet: Tools and Concepts
| Term | Concept |
|---|---|
| SLI | Metric you measure for reliability. |
| SLO | Target reliability goal for engineering. |
| Error Budget | Allowed failure window (100% minus SLO). |
| Toil | Manual, repetitive operational work to automate away. |
| Skaffold | Local dev tool and CD engine for Cloud Deploy. |
| Kustomize | YAML overlays for staging vs production configs. |
| Binary Authorization | Enforce signed, trusted containers only. |
| Cloud Build | Serverless CI for builds and tests. |
| Cloud Deploy | Managed CD release pipelines. |
| Managed Prometheus | Prometheus metrics without self-hosting. |
Flashcards
DevOps delivery, SRE discipline, and observability essentials
Question Text
Click to reveal answerAnswer Text
CI/CD strategy quick view
Pick the delivery model based on governance, rollout needs, and team autonomy.
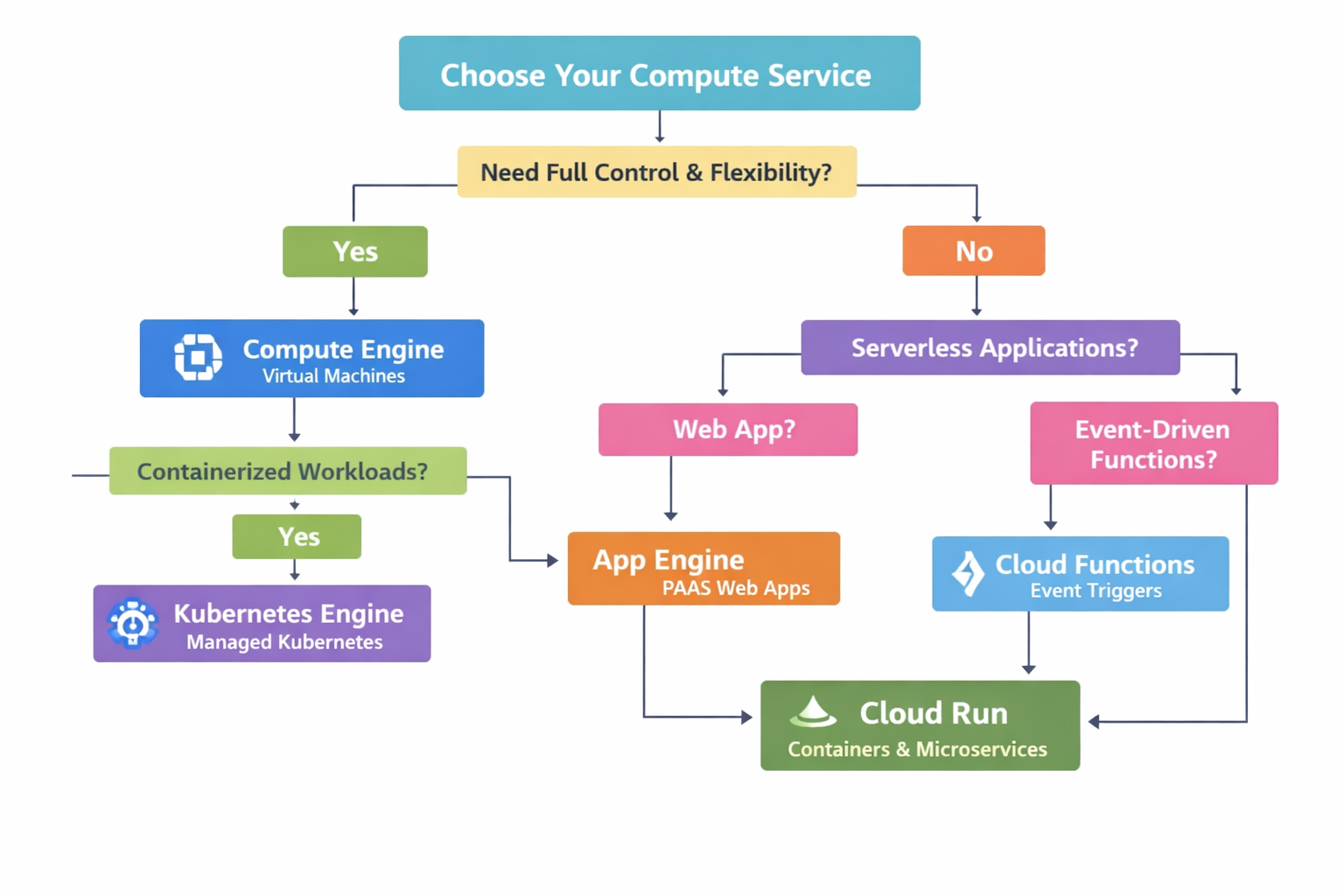
Cloud Build + Cloud Deploy
- Managed CI with approvals
- Canary, blue/green, or rolling
- Best for GKE and Cloud Run
GitOps for GKE
- Declarative config with Config Sync
- Argo CD or Flux integration
- Multi-cluster consistency
Hybrid tooling
- Jenkins, Git, or Packer
- Artifact Registry as hub
- Secure supply chain controls
Pipeline security checklist
- Scan images with Artifact Analysis and block risky builds.
- Enforce Binary Authorization and SLSA provenance for releases.
- Scope IAM per environment and use Workload Identity Federation.
- Store secrets in Secret Manager, keys in Cloud KMS or Certificate Manager.
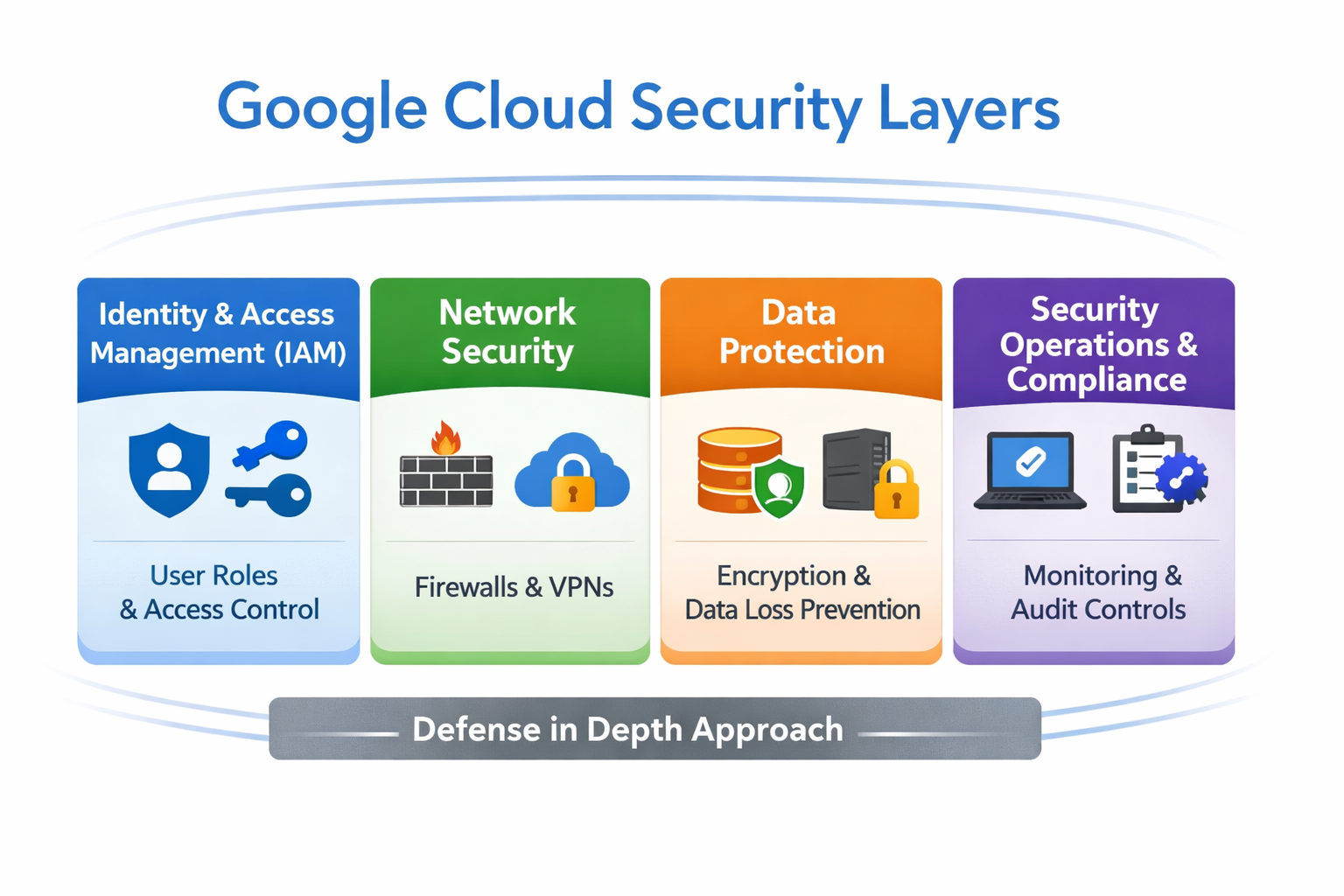
Observability and incident response map
Logs + Metrics + Traces
Use Cloud Logging, Cloud Monitoring, and Trace with OpenTelemetry for end-to-end visibility.
Alerts + Runbooks
Tie SLO-based alerts to runbooks and on-call tools like PagerDuty or webhooks.
Exam clue
If the question mentions SLOs and burn rates, answer with Cloud Monitoring alert policies and error budgets.