Course Introduction
Professional certification
Google Professional Cloud Developer
Build and deploy secure, scalable cloud-native applications. This guide tracks the official exam objectives with deep service choices, deployment patterns, and troubleshooting playbooks.
Want to pass faster?
Get practice tests + the latest deals/discount codes
Get the latest from Cloud-Edify
Get two free courses coupons. Curated learning content, tools, and deal alerts—straight to your inbox.
Exam details (quick view)
Domains (by exam guide)
Design to scale
Choose Cloud Run, GKE, or Compute Engine based on latency, traffic, and ops needs.
Secure by default
Secrets, IAM, service auth, and vulnerability response baked into the lifecycle.
Build & deploy
Cloud Build pipelines, Artifact Registry, and release strategies for Cloud Run and GKE.
Observability
Instrument metrics, logs, traces, and error reporting for fast triage.
Official Exam Objectives
Master cloud-native design, build/test workflows, deployments, integrations, and observability across core Google Cloud services.
Exam Overview
Length: 2 hours
Format: 50-60 multiple choice and multiple select questions
Prereqs: one general-purpose language + CLI tools (gcloud, kubectl, gsutil)
Case studies: scenario-based questions (e.g., HipLocal)
Section 1: Design (Scalable + Reliable)
Architecture and data choices.
High-performance apps & APIs
Microservices: loose coupling, statelessness, decomposition.
API design: REST vs gRPC; gRPC for performance and streaming.
Scaling: horizontal vs vertical; async with Pub/Sub.
State: externalize to Firestore or Memorystore.
Secure applications
IAM: service accounts, least privilege, Workload Identity.
Auth: Identity Platform, IAP.
Encryption: CMEK with Cloud KMS.
Data management
SQL: Cloud SQL for regional, Spanner for global scale.
NoSQL: Firestore (doc), Bigtable (throughput).
Object storage: GCS classes from Standard to Archive.
Section 2: Build & Test
Inner loop and CI/CD.
Dev environments
Cloud Shell: browser shell with gcloud.
Cloud Code: IDE tooling for deploy/debug.
Emulators: Firestore/PubSub/Bigtable for local testing.
CI/CD
Cloud Build: cloudbuild.yaml, build Docker images, deploy to Cloud Run or GKE.
Artifact Registry: replaces Container Registry; supports Docker, Maven, npm.
Testing
Unit vs integration: mock services vs emulators.
Performance: load testing to find bottlenecks.
Section 3: Deploy
Release strategies and compute.
Deployment strategies
Blue/green: reduce downtime.
Canary: split traffic for safe rollout.
Rolling: standard in GKE.
Compute services
Cloud Run: stateless containers, scale to zero.
GKE: Autopilot vs Standard, deployments and services.
App Engine: Standard vs Flexible.
Cloud Functions: event-driven triggers.
Section 4: Integrate
Connect services and APIs.
Application integration
Pub/Sub: push vs pull, dead-letter queues.
Cloud Tasks: rate limiting and retries.
Cloud Scheduler: cron jobs.
API integration
Gateway: API Gateway / Apigee.
Client libraries: prefer idiomatic SDKs vs raw REST.
Error handling: exponential backoff.
Section 5: APM / Observability
Logging, monitoring, tracing.
Cloud Operations suite
Logging: structured logs, sinks to BigQuery, Pub/Sub, GCS.
Monitoring: metrics, alerts, uptime checks.
Trace: latency analysis across services.
Profiler/Debugger: low-overhead CPU/mem insights (note deprecations).
Key Concepts Cheat Sheet
Cloud Run
Stateless containers, per-request billing, scale to zero.
GKE
Microservices orchestration, Autopilot vs Standard.
Cloud Functions
Event-driven glue code for Pub/Sub or Storage.
Pub/Sub
Global async messaging, decoupling services.
Firestore
NoSQL doc DB with real-time sync and offline.
Cloud Spanner
Global SQL with strong consistency.
BigQuery
Serverless warehouse for analytics.
Flashcards
Cloud developer service choices and defaults
Question Text
Click to reveal answerAnswer Text
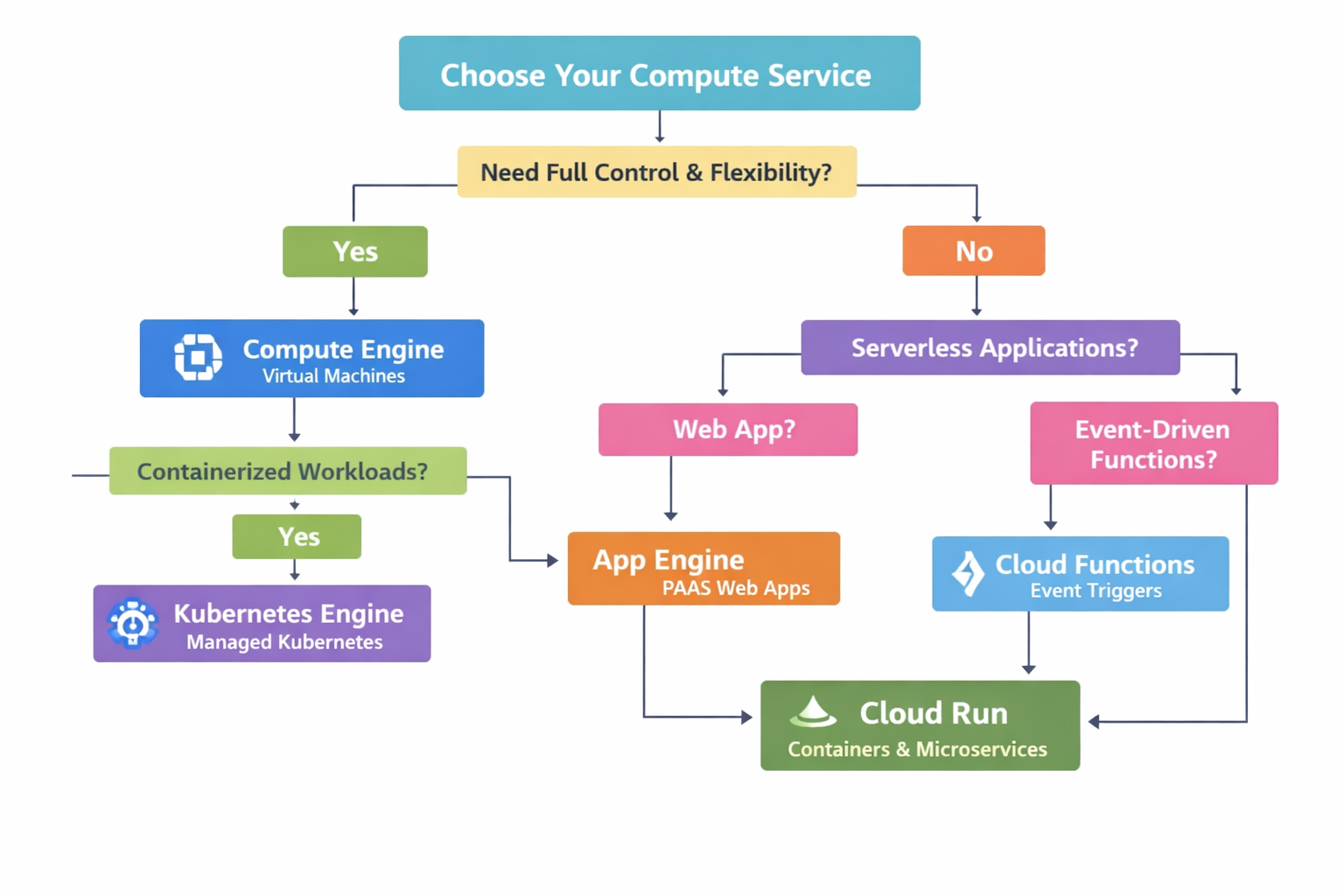
Platform selection quick view
Pick the runtime based on operations overhead and control needs.
Cloud Run
- HTTP-driven or event-triggered
- Scale to zero, minimal ops
- Fast deployment from source
GKE
- Complex microservices
- Service mesh and policies
- Advanced autoscaling
Compute Engine
- Legacy workloads or custom OS
- Full control over networking
- MIGs for scale
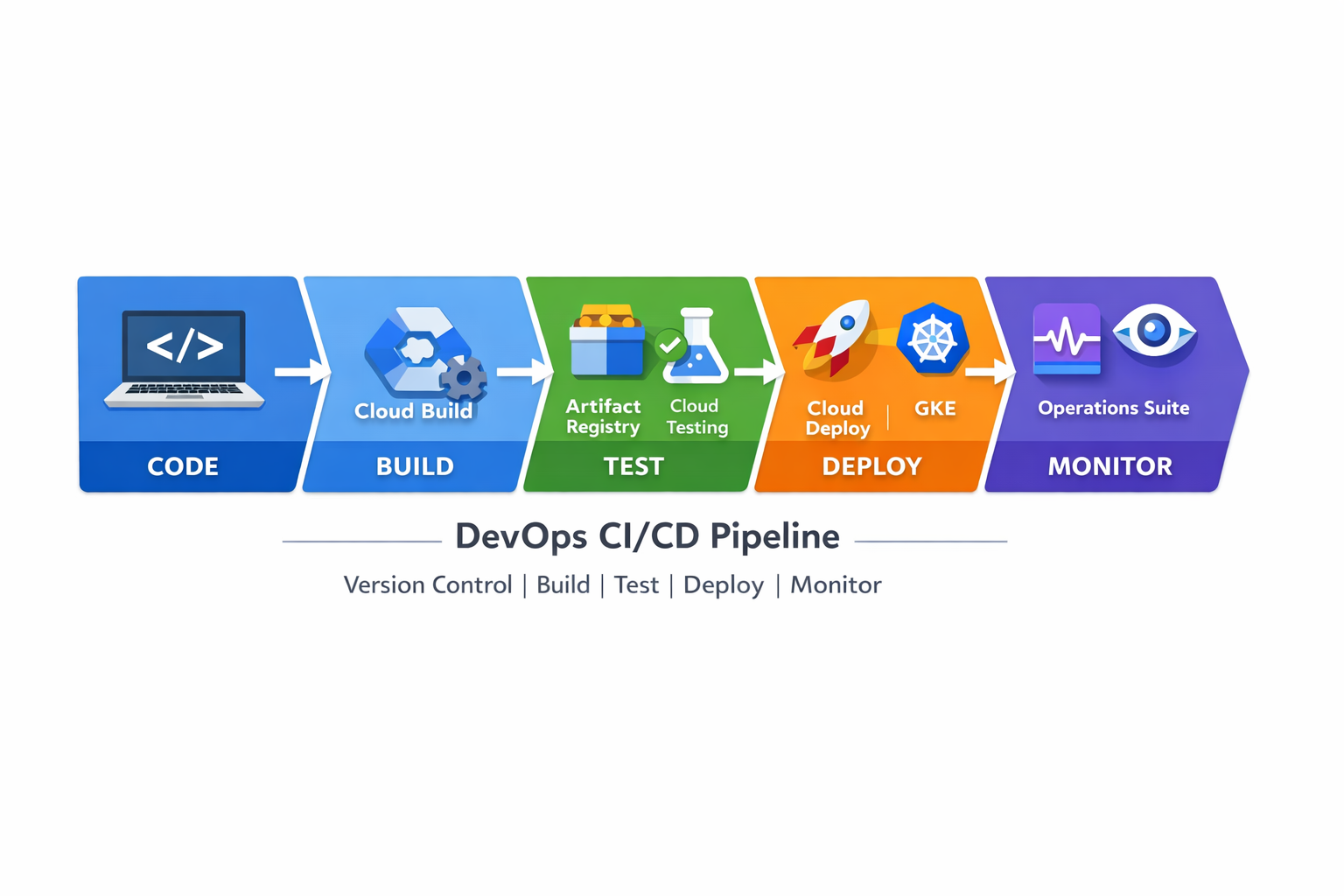
CI/CD pipeline reference
A typical delivery flow: source -> build/test -> artifact -> deploy -> observe. Use it to reason about triggers, artifacts, approvals, and rollbacks.
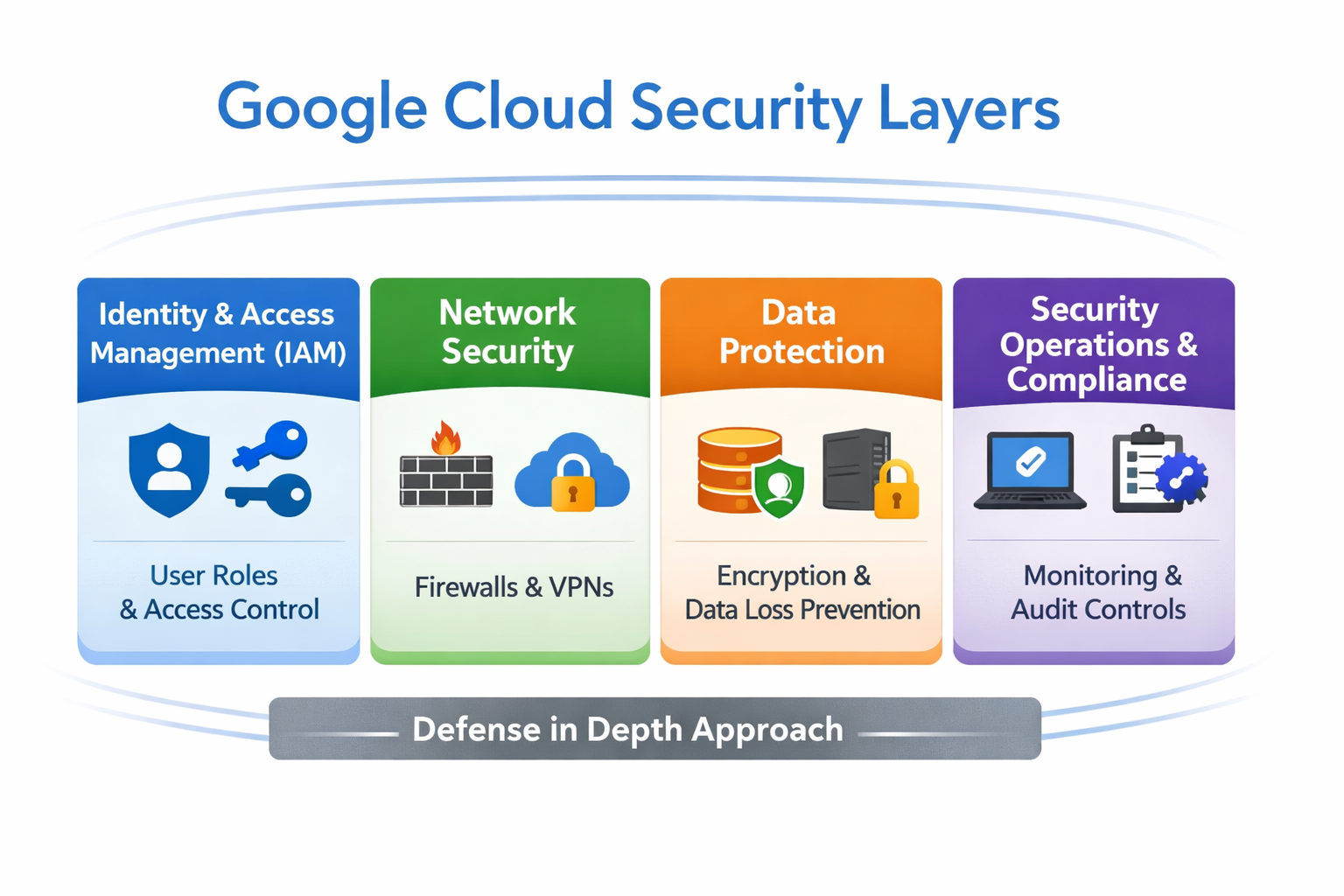
Security and API protection layers
- Use IAM + service accounts for service-to-service auth.
- Put API Gateway or Apigee in front of services for quotas, keys, and auth.
- Use IAP for user-facing apps that need identity-aware access.
- Store secrets in Secret Manager, keys in Cloud KMS.
Eventing and orchestration map
Eventarc + Pub/Sub
Route events from Google services to Cloud Run or Functions with filtering, retries, and dead-letter queues.
Workflows + Tasks
Orchestrate multi-step calls and schedule or throttle background work with retries and rate control.
Exam clue
If the prompt says "decouple producers and consumers," reach for Pub/Sub. If it says "orchestrate multiple services with dependencies," choose Workflows.