Course Introduction
Professional certification
Google Professional Cloud Network Engineer
Design, implement, and manage Google Cloud network infrastructure for availability, scale, and security. This guide follows the official exam objectives with actionable checklists and decision trees.
Want to pass faster?
Get practice tests + the latest deals/discount codes
Get the latest from Cloud-Edify
Get two free courses coupons. Curated learning content, tools, and deal alerts—straight to your inbox.
Exam details (quick view)
Domains (by exam guide)
VPC architecture
Plan subnets, IP ranges, DNS, and Shared VPC for multi-project networks.
Hybrid connectivity
Choose Interconnect or VPN and design HA routing.
Traffic control
Pick the right load balancer, CDN, and routing policy.
Network security
Cloud Armor, Cloud NGFW, and secure egress controls.
Exam Guide + Network Architecture
Design and operate resilient network topologies with hybrid connectivity, secure perimeters, and the right load balancing choices.
Exam Overview
Length: 2 hours
Format: 50-60 multiple choice and multiple select questions
Prerequisites: OSI model, CIDR, routing (BGP), and DNS
Focus: hybrid connectivity, VPC design, and load balancing selection
Exam Domains (6 Sections)
Open each section for key objectives.
1) Designing and planning VPC networks
VPC architecture: default, auto, and custom mode; Shared VPC and VPC peering constraints.
IP planning: secondary ranges for GKE, Private Google Access, and Private Service Connect.
2) Implementing a VPC network
Routing: system routes, static routes, Cloud Router regional vs global mode.
GKE networking: VPC-native clusters, Dataplane V2, and control plane authorized networks.
3) Configuring managed network services
Load balancing: global vs regional, layer 7 vs layer 4, proxy vs passthrough.
Cloud DNS: split-horizon, DNS peering, inbound and outbound forwarding.
4) Hybrid and multi-cloud connectivity
Cloud VPN: HA VPN, route-based vs policy based tunnels.
Interconnect: dedicated vs partner, direct peering, and Cloud Router BGP.
5) Network security
Cloud Armor: WAF and DDoS protection with rate limiting.
Firewalls: VPC firewall rules, hierarchical policies, Cloud NGFW and IPS.
VPC Service Controls: service perimeters against data exfiltration.
6) Network operations and observability
Network Intelligence Center: connectivity tests, topology view, firewall insights.
Logging: VPC flow logs and packet mirroring for deep inspections.
Key Focus Areas
- Pick the right hybrid connectivity option: VPN vs Interconnect.
- Design Shared VPC and peering with clear routing boundaries.
- Select the correct load balancer type and scope.
- Harden perimeters with Armor, NGFW, and VPC SC.
Cheatsheet: Comparisons
| Feature | Cloud VPN | Interconnect |
|---|---|---|
| Traffic | Encrypted over public internet | Private circuit (encryption optional) |
| Max speed | 3 Gbps per tunnel | 10-100 Gbps dedicated |
| SLA | 99.99% (HA VPN) | 99.99% dedicated, 99.9% partner |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| LB type | Scope | Best use case |
|---|---|---|
| External HTTP(S) | Global | Web apps, CDN, multi-region |
| External TCP/UDP | Regional | Gaming, VoIP, passthrough traffic |
| Internal HTTP(S) | Regional | Internal microservices |
| Internal TCP/UDP | Regional | Legacy apps, internal databases |
| Connection | Transitive routing | Use case |
|---|---|---|
| VPC Peering | No | Connect two VPCs directly |
| Cloud VPN | Yes with BGP | On-prem or multi-cloud routing |
| Shared VPC | Same network | Centralized network with multiple projects |
Course Overview
Focus areas from the official exam guide.
Flashcards
Network Engineer service choices and best practices
Question Text
Click to reveal answerAnswer Text
Network decision trees
Click a title to show or hide the diagram. Click the diagram to zoom.
Load balancer selection
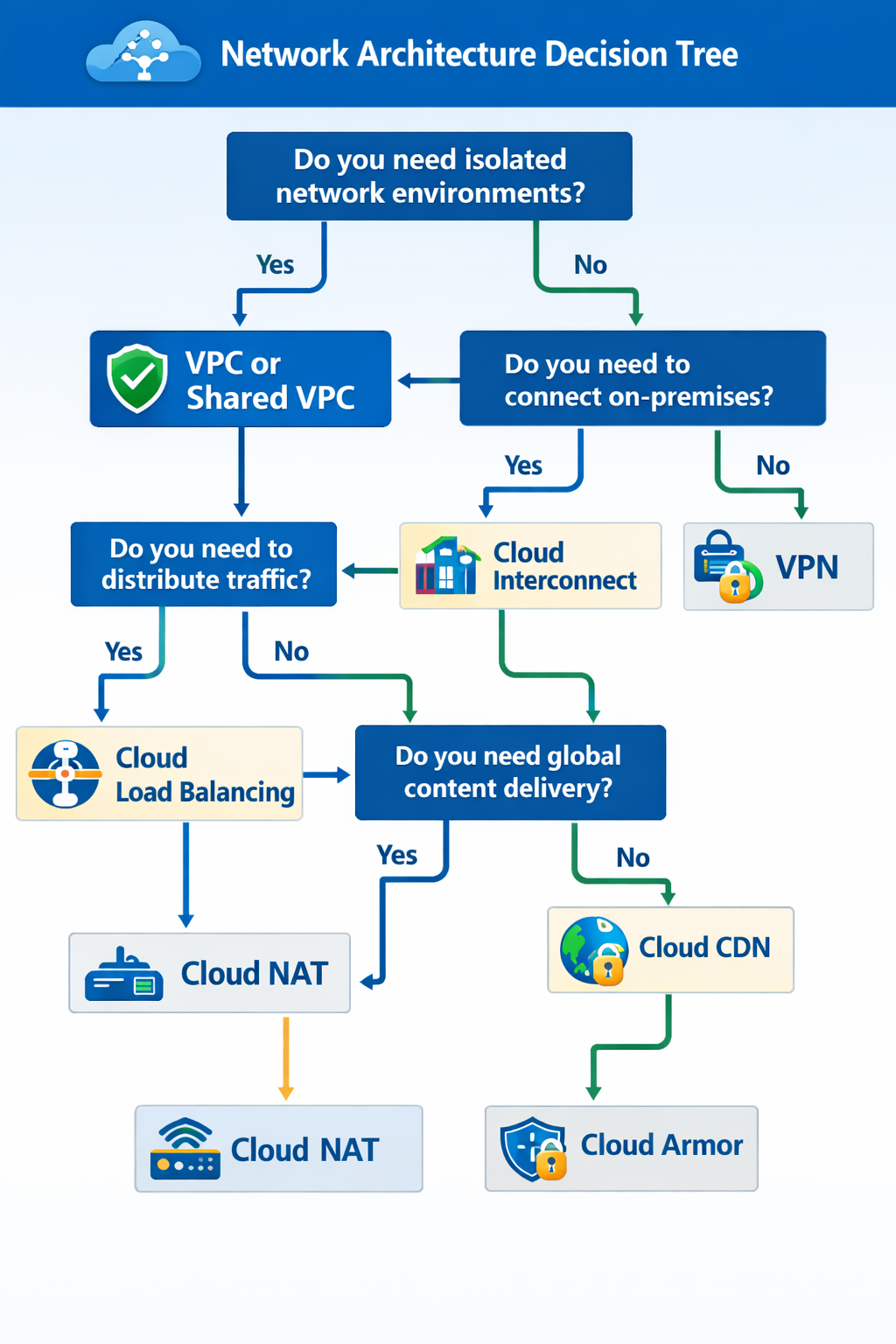
Click the diagram to zoom.
Hybrid connectivity choice

Click the diagram to zoom.
Network security controls

Click the diagram to zoom.