Course Introduction
Professional certification
Google Professional Data Engineer
Design, build, and operate data systems on Google Cloud. This guide focuses on pipelines, storage/processing choices, security, and the exam scenarios you will face.
Want to pass faster?
Get practice tests + the latest deals/discount codes
Get the latest from Cloud-Edify
Get two free courses coupons. Curated learning content, tools, and deal alerts—straight to your inbox.
Storage & models
Choose between BigQuery, Bigtable, Spanner, Cloud SQL based on consistency, scale, and latency.
Pipelines
Batch/streaming patterns with Dataflow, Pub/Sub, Dataproc, and Composer control.
Security & governance
IAM, CMEK, VPC SC, lineage, and data quality checkpoints.
Status
Interactive guide is live - more labs and flashcards are coming.
Official Exam Objectives
Focus on design, implementation, and operationalization of data pipelines and ML models on Google Cloud.
Exam Overview
Length: 2 hours
Format: 50-60 multiple choice and multiple select questions
Prereqs: strong SQL + Python/Java, distributed systems + data modeling.
Focus: select the right service based on cost, latency, throughput, access patterns.
Section 1: Designing Data Processing Systems
Storage + pipelines.
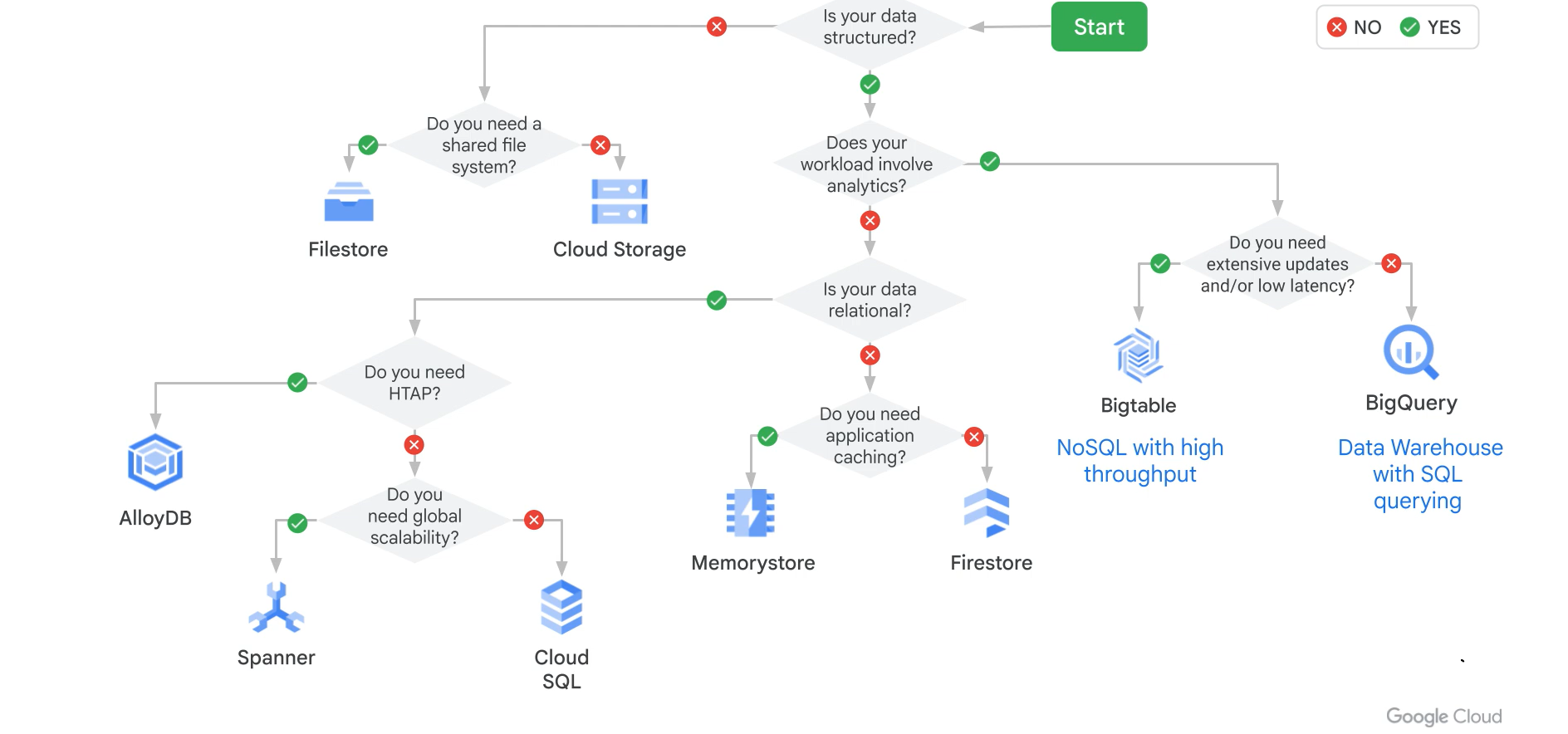
Selecting the right storage
BigQuery: serverless OLAP; partitioning + clustering for cost/perf.
Bigtable: wide-column, sub-10ms latency; row key design matters.
Spanner: global SQL, strong consistency.
Cloud SQL: regional OLTP and lift & shift.
GCS: data lake storage + lifecycle tiers.
Designing data pipelines
Batch vs streaming: bounded vs unbounded data.
Pub/Sub: ingestion layer; ordering keys when order matters.
Dataflow: Beam for batch/stream; windows, watermarks, triggers.
Section 2: Building & Operationalizing Pipelines
ETL, orchestration, migration.
Build pipelines
Dataflow: autoscaling, templates.
Dataproc: lift & shift Hadoop/Spark; preemptibles for workers.
Cloud Fusion: no-code ETL.
Orchestration
Composer: Airflow DAGs across services.
Migration
Transfer Service: S3/Azure/HTTP to GCS.
Transfer Appliance: petabyte migrations.
BQ Data Transfer: SaaS ingestion.
Section 3: Operationalizing ML
Pre-built, BQML, Vertex AI.
Pre-built ML APIs
Vision, Speech, NLP, Video, Translation: choose first for standard use cases.
BigQuery ML
Use case: SQL-first modeling for data analysts.
Models: regression, k-means, matrix factorization, time series.
Vertex AI
AutoML: low-code training.
Training: custom jobs (TF/PyTorch).
Feature Store: avoid training/serving skew.
Pipelines: reproducible MLOps workflows.
Section 4: Ensuring Solution Quality
Security + monitoring.
Security & compliance
IAM: dataset/table/row-level security; policy tags for columns.
DLP: discover and mask PII.
CMEK: customer-managed keys for BigQuery/GCS.
Monitoring & optimization
Monitoring: alerts for failures and latency.
Best practices: avoid SELECT *, use partitioning/clustering, denormalize.
Cheatsheet: Which Service Should I Use?
SQL analytics on petabytes
BigQuery
Low latency + high throughput writes
Bigtable
Global consistency (banking/OLTP)
Spanner
Lift & shift MySQL/Postgres
Cloud SQL
Lift & shift Hadoop/Spark
Dataproc
Serverless batch/stream processing
Dataflow
Orchestrating workflows/DAGs
Cloud Composer
Streaming ingestion
Pub/Sub
ML for SQL users
BigQuery ML
No-code ETL
Cloud Fusion
Flashcards
Test your knowledge of GCP Services
Question Text
Click to reveal answerAnswer Text
Architecture Decision Diagrams
Click on any diagram title to show/hide the diagram.
Storage Decision
Pipeline & Ingestion

ML & GenAI Strategy

Data Transfer & Migration
