Course Introduction
Professional certification
Google Professional Machine Learning Engineer
Design, train, serve, and monitor ML systems on Google Cloud. This guide follows the official objectives with clear decision points across low-code AI, pipeline orchestration, and responsible AI.
Want to pass faster?
Get practice tests + the latest deals/discount codes
Get the latest from Cloud-Edify
Get two free courses coupons. Curated learning content, tools, and deal alerts—straight to your inbox.
Exam details (quick view)
Domains (by exam guide)
Low-code AI
BigQuery ML, AutoML, and Vertex AI Model Garden to ship fast prototypes.
Data and features
Organize datasets, feature stores, and privacy controls for reusable pipelines.
Train and serve
Custom training, distributed hardware, and scalable endpoints.
Monitoring and RAI
Model monitoring, drift detection, and responsible AI practices.
Interactive Exam Guide + GenAI Focus
Build ML systems that scale from low-code prototypes to production pipelines with GenAI, MLOps, and responsible AI practices.
Exam Overview
Length: 2 hours
Format: 50-60 multiple choice and multiple select questions
Prerequisites: Python, Cloud SQL, MLOps fundamentals
v3.1 updates: Generative AI, RAG, and Vertex AI Agent Builder emphasis
Exam Domains (6 Sections)
Open each section for key objectives.
1) Architecting low-code AI solutions (13%)
BQML: train and serve models in SQL for forecasting and classification.
GenAI and Model Garden: Gemini, PaLM, Llama with Agent Builder and RAG.
AutoML: custom tabular, image, text, and video models without code.
2) Collaborating to manage data and models (14%)
Feature store: point-in-time feature lookups and training-serving consistency.
Data privacy: Cloud DLP masking before training.
Experiment tracking: Vertex AI Experiments and TensorBoard.
3) Scaling prototypes into ML models (18%)
Transfer learning: fine-tune Model Garden models.
Distributed training: data parallelism, model parallelism, and parameter servers.
Hardware: GPUs for deep learning, TPUs for large TensorFlow/JAX workloads.
4) Serving and scaling models (20%)
Serving: online endpoints vs batch prediction.
Scaling: autoscaling by CPU/QPS and model quantization.
Private endpoints: secure serving in a VPC.
5) Automating and orchestrating ML pipelines (22%)
Pipelines: Vertex AI Pipelines, TFX, Cloud Composer for orchestration.
CI/CD: retrain on drift with Cloud Build and automated triggers.
Metadata: Vertex ML Metadata for lineage and audits.
6) Monitoring AI solutions (13%)
Responsible AI: explainability, fairness, and bias monitoring.
Skew vs drift: detect schema drift and real-world distribution shifts.
How to Use This Guide
- Mark off topics as you master them.
- Answer self-check questions to test recall.
- Apply scenario challenges to real-world cases.
Cheatsheet: Rapid Review
| Technology | Best Use Case |
|---|---|
| Vertex AI Agent Builder | Rapid RAG apps, chatbots, and search experiences. |
| BigQuery ML | SQL-only ML models for structured data. |
| Vertex AI Pipelines | Serverless MLOps orchestration on GCP. |
| Feature Store | Training-serving consistency and reusable features. |
| Dataflow | Batch and streaming preprocessing at scale. |
| Model Garden | Discover and deploy foundation models (LLMs). |
Flashcards
ML architecture, training, and monitoring essentials
Question Text
Click to reveal answerAnswer Text
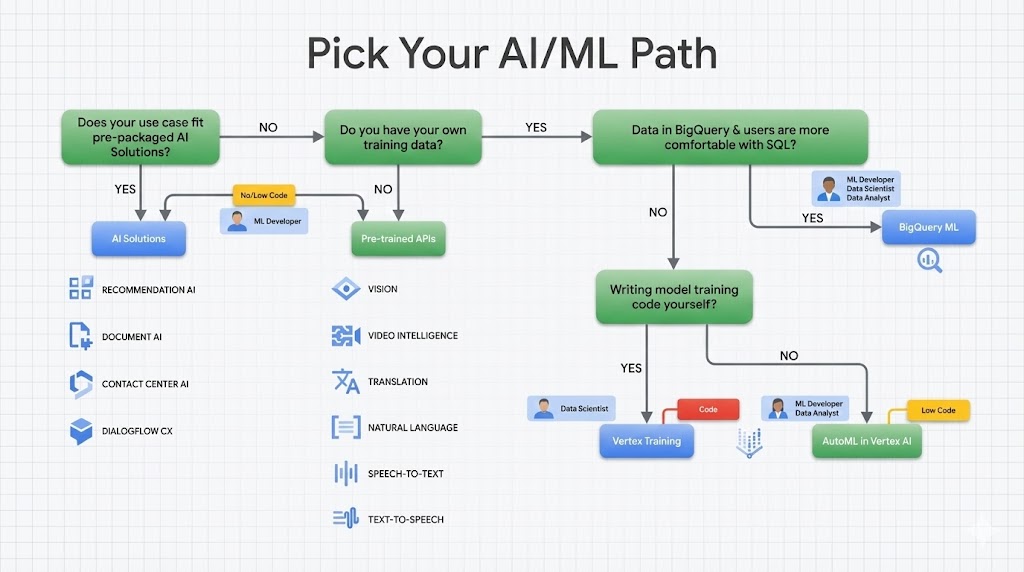
Model development path
Choose the fastest path from prototype to production based on data and model needs.
BigQuery ML
- SQL-first modeling
- Fast experimentation
- Great for tabular problems
AutoML
- Managed training and tuning
- Image, text, tabular, video
- Quick baseline models
Custom training
- Vertex AI custom jobs
- Full framework control
- Scale with GPUs/TPUs
Training and data pipeline checklist
- Use Dataflow, TFX, or BigQuery for consistent preprocessing.
- Store reusable features in Vertex AI Feature Store.
- Track experiments and metadata in Vertex AI Experiments.
- Use Cloud KMS and IAM to protect datasets and notebooks.
Serving and monitoring map
Batch + Online Serving
Use Vertex AI Prediction for online endpoints and Dataflow or BigQuery ML for batch.
Monitoring + Drift
Use Vertex AI Model Monitoring and Explainable AI to track skew and performance.
Exam clue
If the prompt says training-serving skew, use Vertex AI Model Monitoring and feature attribution drift checks.