Course Introduction
Foundational certification
Google Cloud Digital Leader
Explain Google Cloud value, core products, and responsible use of AI/ML to business stakeholders. Use this guide for concise stories, visuals, and exam-ready explanations.
Want to pass faster?
Get practice tests + the latest deals/discount codes
Get the latest from Cloud-Edify
Get two free courses coupons. Curated learning content, tools, and deal alerts—straight to your inbox.
Free Community Video Course
A comprehensive video series to help you prepare for the Google Cloud Digital Leader exam.
Watch NowBusiness outcomes
Map cloud capabilities to cost, reliability, security, and innovation goals.
Product choices
Visual decision trees for compute, storage, networking, and analytics.
AI/ML essentials
Responsible AI principles, use cases, and when to choose Vertex AI or prebuilt APIs.
Status
Full interactive guide is live; new practice sets are added regularly.
Cloud Computing Fundamentals
Focus on core cloud concepts, Google Cloud services, security foundations, billing models, and modernization patterns.
Summary
This guide covers essential cloud computing fundamentals with a Google Cloud focus: core services, security responsibilities, cost models, and modernization pathways.
Key Concepts
Open each topic to review the essentials.
Cloud service models
IaaS: raw compute/storage/networking (Compute Engine).
PaaS: managed platform (App Engine, Cloud Run).
SaaS: fully managed apps (Workspace).
FaaS: event-driven serverless functions (Cloud Functions).
Resource hierarchy
Organization: root node for policy and billing governance.
Folders: group projects by team or department.
Projects: containers for resources, billing, and IAM.
Core products
Compute: Compute Engine, App Engine, Cloud Run, GKE.
Storage: Cloud Storage classes (Standard/Nearline/Coldline/Archive).
Databases: Cloud SQL, Spanner, Firestore, Bigtable.
Analytics: BigQuery for serverless data warehouse analytics.
Security & compliance
Shared responsibility: Google secures the cloud; customers secure data and access.
IAM: who can do what on which resource; least privilege.
Security services: Cloud Armor, IAP, DLP.
Key Questions
Reveal the answer you should give on the exam.
Compute Engine vs Cloud Run?
Compute Engine = VMs with OS control; Cloud Run = serverless containers that scale to zero.
Spanner vs Cloud SQL?
Spanner for global scale and strong consistency; Cloud SQL for regional relational workloads.
Pay-as-you-go vs traditional procurement?
Cloud OpEx = usage-based; traditional = upfront CapEx.
Purpose of Organization node?
Root of the resource hierarchy for centralized policy management.
Storage class for annual access?
Archive Storage (lowest cost for data accessed yearly).
How does Cloud Load Balancing improve reliability?
Distributes traffic across backends/regions to handle spikes and failover.
Cost estimate before migration?
Use the Google Cloud Pricing Calculator.
Shared responsibility in cloud security?
Google secures the infrastructure; customers secure data, IAM, and configs.
Best service for VMware lift-and-shift?
Google Cloud VMware Engine.
Region vs Zone?
Regions are geographic areas; zones are isolated data centers within a region.
Vocabulary
Elasticity
Resources scale up/down automatically with demand.
High Availability (HA)
Design for continued operation despite failures.
Latency
Delay before data transfer begins.
SLA
Provider uptime commitment.
TCO
Total cost to acquire and operate technology.
Zero Trust
Assume no user/device is trusted by default.
Microservices
Apps built from small, independent services.
Knowledge Check
Fundamentals and core concepts
Question Text
Click or press Enter/Space to reveal answerAnswer Text
Decision Scenarios
Click a title to show/hide the diagram. Click the diagram to zoom.
Compute service model

Click the diagram to zoom.
Cloud model overview

Click the diagram to zoom.
Data store choices
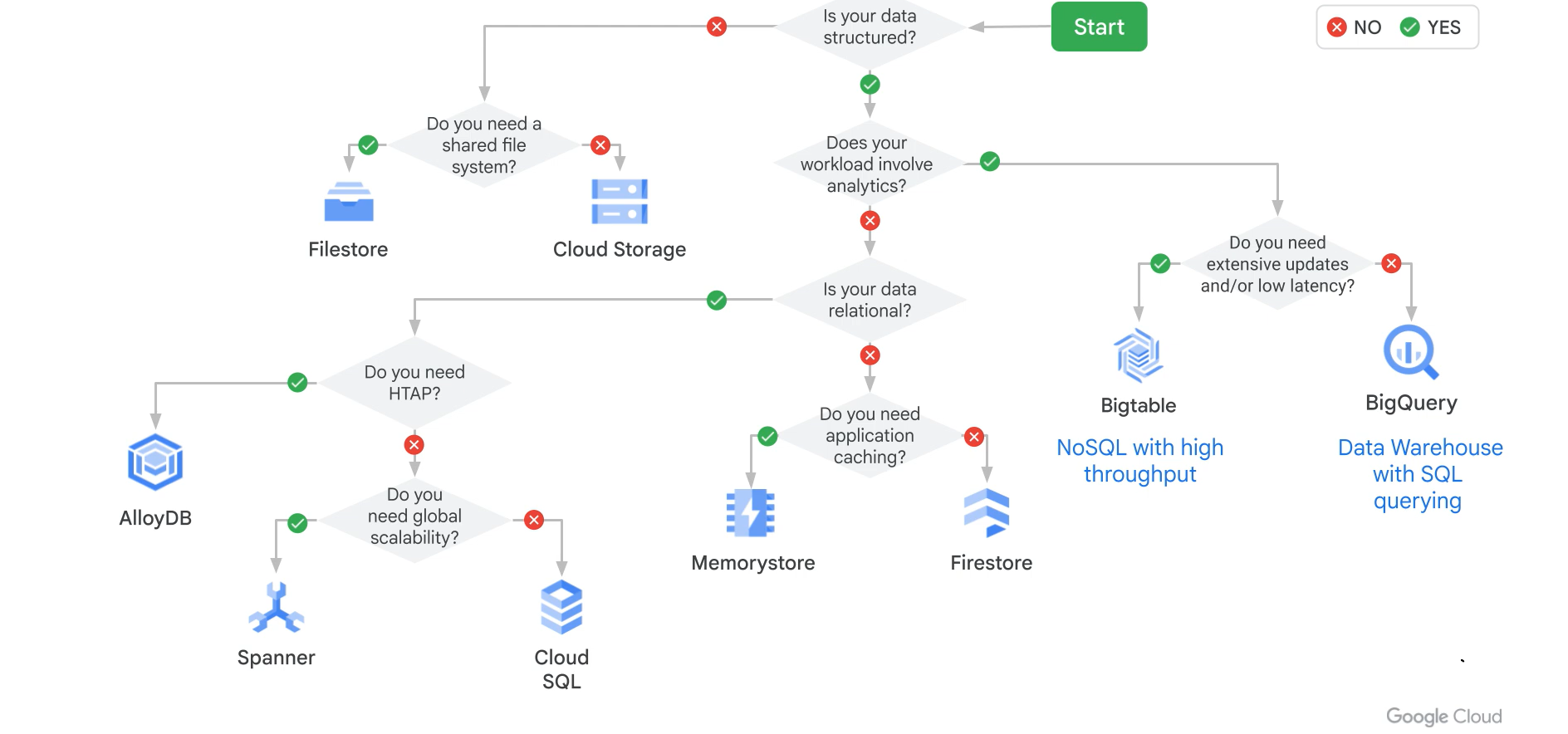
Click the diagram to zoom.
Data transfer options

Click the diagram to zoom.
Analytics pipeline overview

Click the diagram to zoom.